Vertical Tabs
Rakhine State
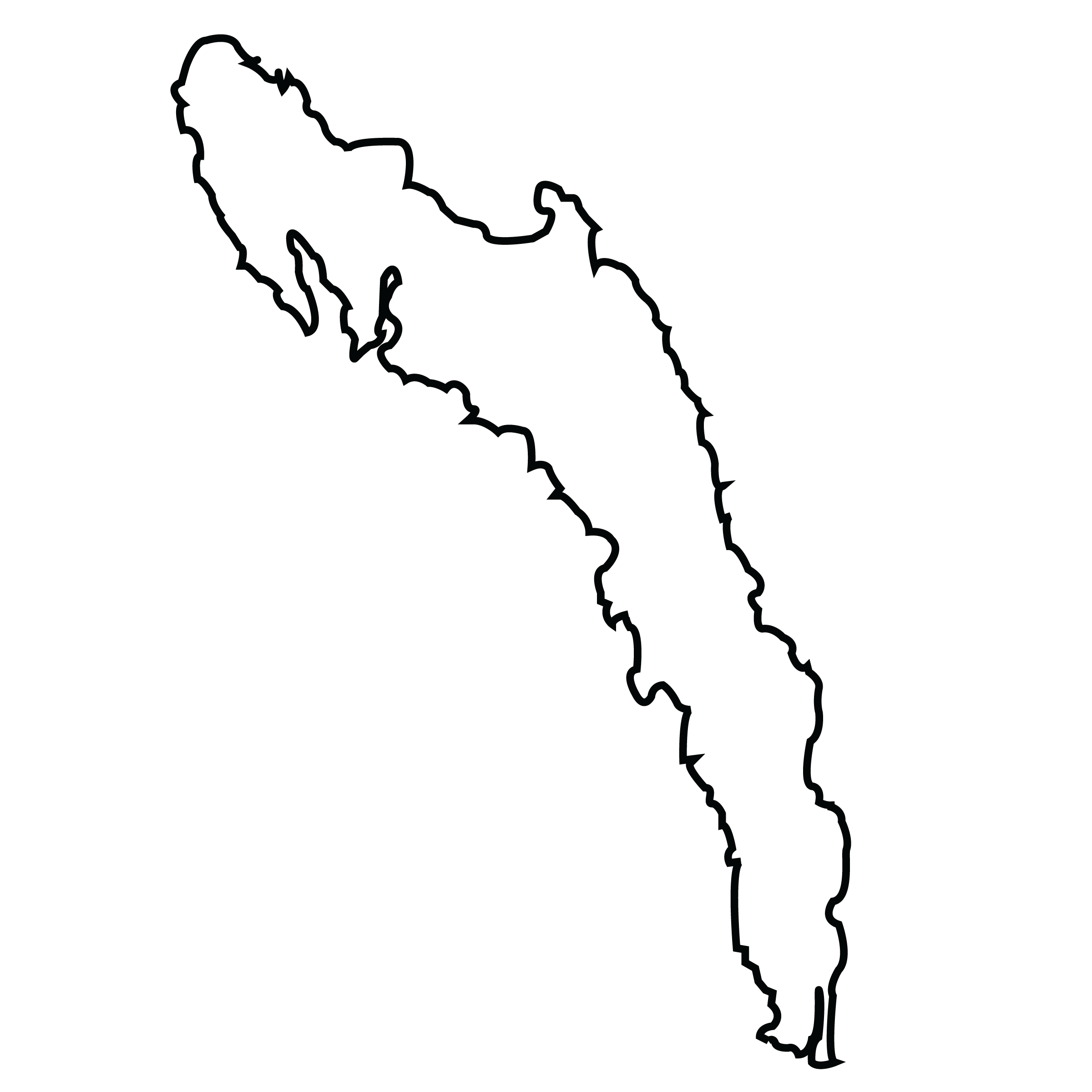
Rakhine State is a state in Myanmar. Situated on the western coast, it is bordered by Chin State in the north, Magway Region, Bago Region and Ayeyarwady Region in the east, the Bay of Bengal to the west, and the Chittagong Division of Bangladesh to the northwest. It is located approximately between latitudes 17°30' north and 21°30' north and east longitudes 92°10' east and 94°50' east. The Arakan Mountains, which rise to 3,063 metres (10,049 ft) at Victoria Peak, separate Rakhine State from central Burma. Off the coast of Rakhine State there are some fairly large islands such as Cheduba and Myingun Island. Rakhine State has an area of 36,762 square kilometres (14,194 sq mi) and its capital is Sittwe.
Rakhine State, like many parts of Burma, has a diverse ethnic population. Official Burmese figures state Rakhine State's population as 3,118,963. The ethnic Rakhine make up the majority. The Rakhine reside mainly in the lowland valleys as well as Ramree and Manaung (Cheduba) islands. A number of other ethnic minorities like the Rohingya, Chin, Mro, Chakma, Khami, Dainet, Bengali Hindu and Maramagri inhabit mainly in the hill regions of the state. Most of the Tibeto-Burmans living in Rakhine State adhere to Theravada Buddhism. Few roads cross the Arakan Mountains from central Burma to Rakhine State. The three highways that do are the Ann to Munbra (Minbya in Burmese pronunciation) road in central Rakhine, the Toungup to Pamtaung road in south central Rakhine, and the Gwa to Ngathaingchaung road in far southern Rakhine.
Air travel still is the usual mode of travel from Rangoon and Mandalay to Sittwe and Ngapali, the popular beach resort. Only in 1996 was a highway from Sittwe to the mainland constructed. The state still does not have a rail line (although Myanmar Railways has announced a 480-km rail extension to Sittwe from Pathein via Ponnagyun-Kyauttaw-Mrauk U-Minbya-Ann). Rice is the main crop in the region, occupying around 85% of the total agricultural land. Coconut and nipa palm plantations are also important. Fishing is a major industry, with most of the catch transported to Yangon, but some is also exported. Wood products such as timber, bamboo and fuel wood are extracted from the mountains. Small amounts of inferior-grade crude oil are produced from primitive, shallow, hand-dug wells, but there is yet unexplored potential for petroleum and natural gas production.
Tourism is slowly being developed. The ruins of the ancient royal town Mrauk U and the beach resorts of Ngapali are the major attractions for foreign visitors, but facilities are still primitive, and the transportation infrastructure is still rudimentary. While most places in Myanmar suffer from chronic power shortages, in rural states like Rakhine the problem is disproportionately greater. In 2009, the electricity consumption of a state of 3 million people was only 30 MW, or 1.8% of the country's total generation capacity. In December 2009, the military government added three more hydropower plants, Saidin, Thahtay Chaung and Laymromyit, at a cost of over US$800 million. The three plants together can produce 687 MW but the surplus electricity will be distributed to other states and divisions.
See how the Mary K. Yap Foundation is supporting programs like the "Myanmar Orphans" Project ....Learn more >
Copyright © 2014 - 2026 Mary K. Yap Foundation Inc. All rights reserved.
Designed by WTCMM
Languages
- English

- myanmar


